Mathematik-Online-Aufgabensammlung:
|
[Home] [Lexikon] [Aufgaben] [Tests] [Kurse] [Begleitmaterial] [Hinweise] [Mitwirkende] [Publikationen] |
|
Mathematik-Online-Aufgabensammlung: | |
Aufgabe 354: Volumen, Normalen und Schwerpunkt eines Körpers im Vektorfeld |
| A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
Das Vektorfeld
![]() sei definiert durch
sei definiert durch
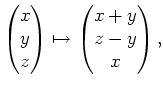
![\fbox{\parbox{5cm}{\rule[-1.5ex]{0pt}{0.8cm}\hfill \hspace{\fill}}}](/inhalt/aufgabe/aufgabe354/img13.png)
![\fbox{\parbox{5cm}{\rule[-1.5ex]{0pt}{0.8cm}\hfill \hspace{\fill}}}](/inhalt/aufgabe/aufgabe354/img13.png)
![$ \mathrm{rot} g = \fbox{\parbox{5cm}{\rule[-1.5ex]{0pt}{0.8cm}\hfill \hspace{\fill}}}$](/inhalt/aufgabe/aufgabe354/img15.png) .
.
![$ \mathrm{div} g = \fbox{\parbox{5cm}{\rule[-1.5ex]{0pt}{0.8cm}\hfill \hspace{\fill}}}$](/inhalt/aufgabe/aufgabe354/img16.png) .
.
![$ v=\fbox{\parbox{5cm}{\rule[-1.5ex]{0pt}{0.8cm}\hfill \hspace{\fill}}}$](/inhalt/aufgabe/aufgabe354/img17.png) .
.
![$\displaystyle \int\limits_{\ \fbox{\parbox{1.5cm}{\rule[-1.5ex]{0pt}{0.5cm}\hfi...
...ox{2cm}{\rule[-1.5ex]{0pt}{0.8cm}\hfill \hspace{\fill}}}\quad
d\varphi\,dr\,dz$](/inhalt/aufgabe/aufgabe354/img18.png)
![\fbox{\parbox{2cm}{\rule[-1.5ex]{0pt}{0.8cm}\hfill \hspace{\fill}}}](/inhalt/aufgabe/aufgabe354/img19.png) .
.
![$ x_{S_P} = \fbox{\parbox{2cm}{\rule[-1.5ex]{0pt}{1cm}\hfill \hspace{\fill}}}\;,\quad y_{S_P}= \fbox{\parbox{2cm}{\rule[-1.5ex]{0pt}{1cm}\hfill \hspace{\fill}}}$](/inhalt/aufgabe/aufgabe354/img21.png) ,
,
![$ z_{S_P}=\fbox{\parbox{2cm}{\rule[-1.5ex]{0pt}{1cm}\hfill \hspace{\fill}}}$](/inhalt/aufgabe/aufgabe354/img22.png)
![$ \iint\limits_{\partial M} g \cdot n\, \mathrm{d}O =
\fbox{\parbox{2cm}{\rule[-1.5ex]{0pt}{0.8cm}\hfill \hspace{\fill}}}$](/inhalt/aufgabe/aufgabe354/img23.png) .
.
(Hierbei sei ![]() der nach außen weisende Normaleneinheitsvektor.)
der nach außen weisende Normaleneinheitsvektor.)
![$ \int_K g \mathrm{d}x =\fbox{\parbox{2cm}{\rule[-1.5ex]{0pt}{0.8cm}\hfill \hspace{\fill}}}$](/inhalt/aufgabe/aufgabe354/img25.png) .
.
siehe auch:
| automatisch erstellt am 2. 9. 2005 |