Mathematik-Online-Lexikon:
|
[Home] [Lexikon] [Aufgaben] [Tests] [Kurse] [Begleitmaterial] [Hinweise] [Mitwirkende] [Publikationen] |
|
Mathematik-Online-Lexikon: | |
Grenzwertbestimmung mit Maple |
| A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z | Übersicht |
> limit ( 1/x, x=infinity);
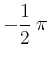
MAPLE geht bei der Berechnung davon aus, dass unbelegte Variablen reell und ungleich 0 sind. Hängt der Grenzwert vom Vorzeichen der Variable ab, so wird ggf. der Grenzwert mit der Signum-Funktion csgn angegeben bzw. bei nicht allgemein bestimmbaren Grenzwerten wird die Eingabe zurückgegeben.
> limit ( arctan(a*x), x=infinity);
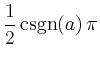
siehe auch:
| automatisch erstellt am 5. 3. 2012 |